in PNGplants database
PNGTreesKey – Pangium edule Reinw. |
Barry Conn (NSW) & Kipiro Damas (LAE).
Guide to trees of Papua New Guinea
Copyright held by the authors, National Herbarium of New South Wales, and Papua New Guinea National Herbarium
Sylloge Plantarum Novarum Itemque Minus Cognitarum a Praestantissimis Botanicis adhuc Viventibus Collecta et a Societate Regia Botanica Ratisbonensi Edita. Ratisbonae [Regensburg] Vol. 2: 13 (1825)
Other Literature: H. Sleumer, Flora Malesiana, Series 1, 36-39 (1954) Fig. 12-16.
Family: Salicaceae
Dicotyledon
Timber Group: Minor hardwood
Field Characters: Large canopy tree (usually up to 25 m high) or Small sub-canopy tree; Bole cylindrical (up to c. 75 cm diam.); crooked (often or leaning) or straight (bole 7-10 m long); buttresses buttresses present; spines spines absent; aerial roots aerial roots absent; stilt roots stilt roots absent; Bark slightly green, brownish grey, or dark brown, slightly rough or smooth, scaly or flaky and fissured or slightly tessellated; Subrhytidome (under-bark) yellow or orange; less than 25 mm thick, 10.0-13.0; bark blaze consisting of one layer; strongly aromatic; onion-like (turnip-like odour); outer blaze white or pale yellow, markings absent; inner blaze white or pale yellow, markings absent; bark exudate (sap) present, colourless, flowing, colour not changing on exposure to air, not sticky; terminal buds not enclosed by leaves.
Indumentum: Complex hairs absent; stinging hairs absent; mature twig indumentum (hairs) present when young or later absent, hairs dense.
Leaves: Leaves clustered at end of branches, spiral (leaves occurring singly at a node and arranged spirally up the branchlet), simple (a leaf composed of a single blade); petiole present, not winged, attached to base of leaf blade, swollen; leaves broadest below middle, (10.0-) 12.0-30.0 (-60.0) cm, 80.0-200.0 (-400.0) cm; symmetric, entire, not dissected or lobed, acuminate, venation pinnate, secondary veins open, prominent, intramarginal veins absent; leaves lower surface pale green, upper surface dark green (glossy), indumentum (hairs) absent (above) or present, indumentum (hairs) dense; absent; domatia absent; stipules absent.
Flowers: Inflorescence axillary, flowers single (female flowers) or flowers on an unbranched axis (mostly male flowers), cones absent; flowers unisexual, unisexual with male and female flowers on different plants, stalked, flowers with many planes of symmetry, 1.5-2.5 mm long, diameter small (up to10 mm diam.); perianth present, with distinct sepals and petals whorls, inner perianth green (pale (bright); (4-) 5-8 (-9), free; stamens 20-25 (-30), present, joined (on flattened disk), free of the perianth; ovary inferior, carpels joined (when more than one), locules 5; styles absent.
Fruits: Infrutescence single or arranged on unbranched axis (often referred to as cones), fruit 150.0-250.0 (-300.0) mm long, brown, not spiny, fleshy, simple, indehiscent, berry (although not a true berry); seeds 20 (c. poisonous, red-brown, embedded in a yellow, custard-like pulp that is strongly aromatic), much more than 10 mm long, not winged, irregular, seed more than 10 mm diam.
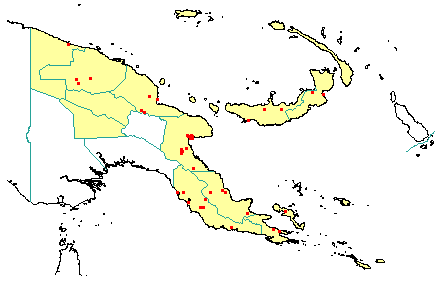
Distribution: West Sepik, East Sepik, Madang, Morobe, Western Highlands, Southern Highlands, Central, Northern, Milne Bay, Papuan Islands, New Britain, New Ireland & Manus.
 | Botanical records in PNGplants database |
Notes: Notes The taxonomic position of this genus is not known, but since it was previously classified in the family Flacourtiaceae, it is here transferred to the family Salicaceae.