in PNGplants database
PNGTreesKey – Ficus trachypison K.Schum. |
Barry Conn (NSW) & Kipiro Damas (LAE).
Guide to trees of Papua New Guinea
Copyright held by the authors, National Herbarium of New South Wales, and Papua New Guinea National Herbarium
Nachträge zur Flora der Deutschen Schutzgebiete in der Südsee 280
Other Literature: C.C. Berg & E.J.H. Corner, Flora Malesiana, Series 1 256-258 (2005) Fig. 50 (map 6).
Family: Moraceae
Dicotyledon
Timber Group: Occasional timber species Tradename: Fig
Field Characters: Large canopy tree (up to 30 m high); Bole markedly fluted (usually at least 50 cm diam.); crooked (bole up to 15 m long); buttresses buttresses present (buttresses mostly up to 1.5 m high); spines spines absent; aerial roots aerial roots absent; stilt roots stilt roots absent; Bark grey or dark brown, rough or smooth, pustular, often lenticels elongated laterally or lenticels elongated vertically; Subrhytidome (under-bark) white, orange, or mottled; less than 25 mm thick, 15.0; bark blaze consisting of one layer; strongly aromatic; spice-like (garlic-like); outer blaze white, pale orange, or pale brown, with stripes, fibrous; inner blaze white, pale orange, or pale brown, with stripes, fibrous; bark exudate (sap) present, orange (pale (honey-coloured) or white/milky, flowing, colour not changing on exposure to air, sticky; terminal buds not enclosed by leaves.
Indumentum: Complex hairs absent; stinging hairs absent; mature twig indumentum (hairs) absent.
Leaves: Leaves spaced along branches, spiral (leaves occurring singly at a node and arranged spirally up the branchlet), simple (a leaf composed of a single blade); petiole present, not winged, attached to base of leaf blade, not swollen; leaves broadest at or near middle or slightly equally broad throughout much of length, (3.0-) 5.0-15.0 (-27.0) cm, 3.5-10.0 (-13.0) cm; almost symmetric, sub entire or crenate (irregularly (usually variously revolute), not dissected or lobed, acuminate (shortly) or obtuse, venation pinnate, secondary veins open, prominent, intramarginal veins absent; leaves lower surface pale green, upper surface dull green, indumentum (hairs) present (coarse to touch, like sand-papery), indumentum (hairs) sparse (hairs whitish to pale brown) or dense; absent; domatia absent (but with cystoliths on both surfaces); stipules present, joined, joined across twigs, almost encircling the twig, leafy, not fringed, large (4-10 mm long), not persistent.
Flowers: Inflorescence axillary (synconia/figs), flowers arising from a single point (with syconium/fig in pairs), flowers single (syconium/fig solitary), or flowers on an unbranched axis (flowers within a synconium/fig), cones absent; flowers unisexual, unisexual with male and female flowers on the same plant, stalked or not stalked, flowers with many planes of symmetry (synconium/fig), with one plane of symmetry (male and female flowers), or completely asymmetric, 3.0-6.0 mm long, diameter small (up to10 mm diam.) (2-3 mm diam.); perianth present, with all sepals and/or petals (hence tepals) similar (membranous), inner perianth red (pale to dark); 3-5, free or some or partly joined (shortly at base); stamens 1 (male flowers), present, free of the perianth; ovary superior, carpels solitary; styles absent (male flowers) or solitary (female flowers), 1.
Fruits: Infrutescence arranged on unbranched axis (syconium/fig solitary, in pairs or in clusters on short-shoots on older wood), fruit 4.0-8.0 mm long, 4.0-10.0 mm diam., purple, dark red, or yellow, not spiny, fleshy, syconium (fig), indehiscent, achene or syconium (fig); seeds 100, barely visible (to 1 mm long), not winged, broad (as wide as long), seed less than 1 mm diam.
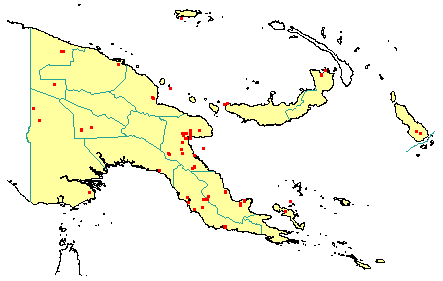
Distribution: West Sepik, East Sepik, Madang, Morobe, Western Highlands, Eastern Highlands, Southern Highlands, Western, Gulf, Central, Northern, Milne Bay, Papuan Islands, New Britain, Manus & Bougainville.
 | Botanical records in PNGplants database |